|
General Cytopathology and Pathology for Cervical Disease Screening
Cytopathology, as a routing and basic work in our Department, is simple, safe, quick, economic and valuable for the cancer screening such as respiratory, digestive, urinary and cervical diseases. In other hand, Cytopathology is great valuable for the screening diagnosis of superficial tumor such as oral and skin cancer, for the supplementary diagnosis of deep tumors such as lung and digestive cancer. For the screening of cervical diseases there is traditional cytology, liquid based cytology, 2th generation gene hybridization capture technique and quick HPV detection system, the occurrence and mortality of late stage cervical carcinoma is lowered as to 50% with using screening.
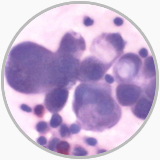
Gastric signet cell carcinoma from ascites |
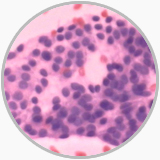
Papillry carcinoma from thyroid gland puncture |
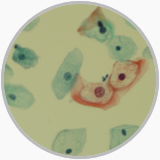
Liquid Based Cytology shows the koilocytes in a cervical low-grad squamous intraepithelial lesion |
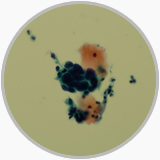
Liquid Based Cytology shows the atypical cells in a cervical high-grad squamous intraepithelial lesion |
Flow Cytometry (FCM) and Flowfluorenscence Activated Cell Sorter (FACS)
FCM is helpful in aiding diagnosis for some pathologically ambiguous cases and, by DNA ploidy analysis may give prognostic information besides tumor grading and staging. Further, a demonstration of tumor cell proliferation cycle by FCM may monitor chemotherapy efficiency of tumor patients. The FCM with multicolor and multichannel gates technique may detect many antigens from a patient and may be used in various lymph-hematologic diseases. With the development of FASC and improvement, a detection of circulation tumor cell (CTC) has received great attention to monitor the tumor patients during and after chemotherapy.
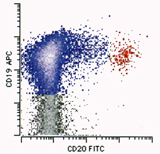
FACS shows CD19+CD20+(blue color) tumor cells in mantle cell lymphoma |
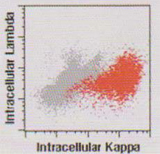
FACS shows Intracellular Kappa positive (red) and Lambda negative tumor cells from a plasma cell neoplasm |
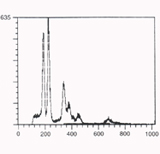
FCM shows heteroploidy from an endometrial carcinoma |
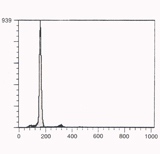
FCM shows diploidy from a normal endometrium |
Electron Microscopy (EM)
Although the role of EM in diagnostic pathology has diminished because of a comprehensive use of IHC, EM remains a powerful tool for tumor diagnostic pathology. It is important for a pathologist to formulate 2-3 definite differential diagnosis entities at light microscopic level and search specifically for these entities under EM. When closely correlated with the gross pathology, clinical and light microscopic features, EM observations may provide many information of differentiation diagnosis: the tonofilaments or intercellular junction may demonstrate a epithelial tumor origin, the intracellular dense body filaments are seen in leiomyoma or leiomyosarcoma, intracellular actin and myosin filaments exist only in rhabdomyoma or rhabdomyosarcoma, neuroendocrine tumor contains special neuroendocrine granules and intracellular melanosomes are aiding in a diagnosis of melanoma. In the renal pathology EM examinations have proved very useful in confirmation and differentiation of various renal diseases.
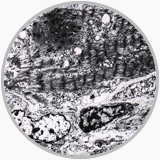
EM shows intracellular cross striation from arhabdomyosarcoma |
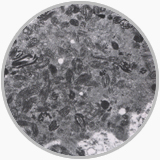
EM shows intracellular melanosomes from amelanoma |
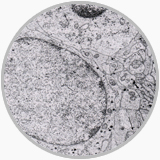
The comlex cytoplasmic processes and electronic dense bodies that exist in neuroblastoma are showed under EM |
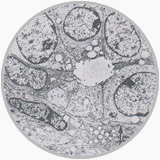
The adenoepithelium and spindle cells in a biphasic synovial sarcoma are noted in EM |
|
